what does glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase do Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase
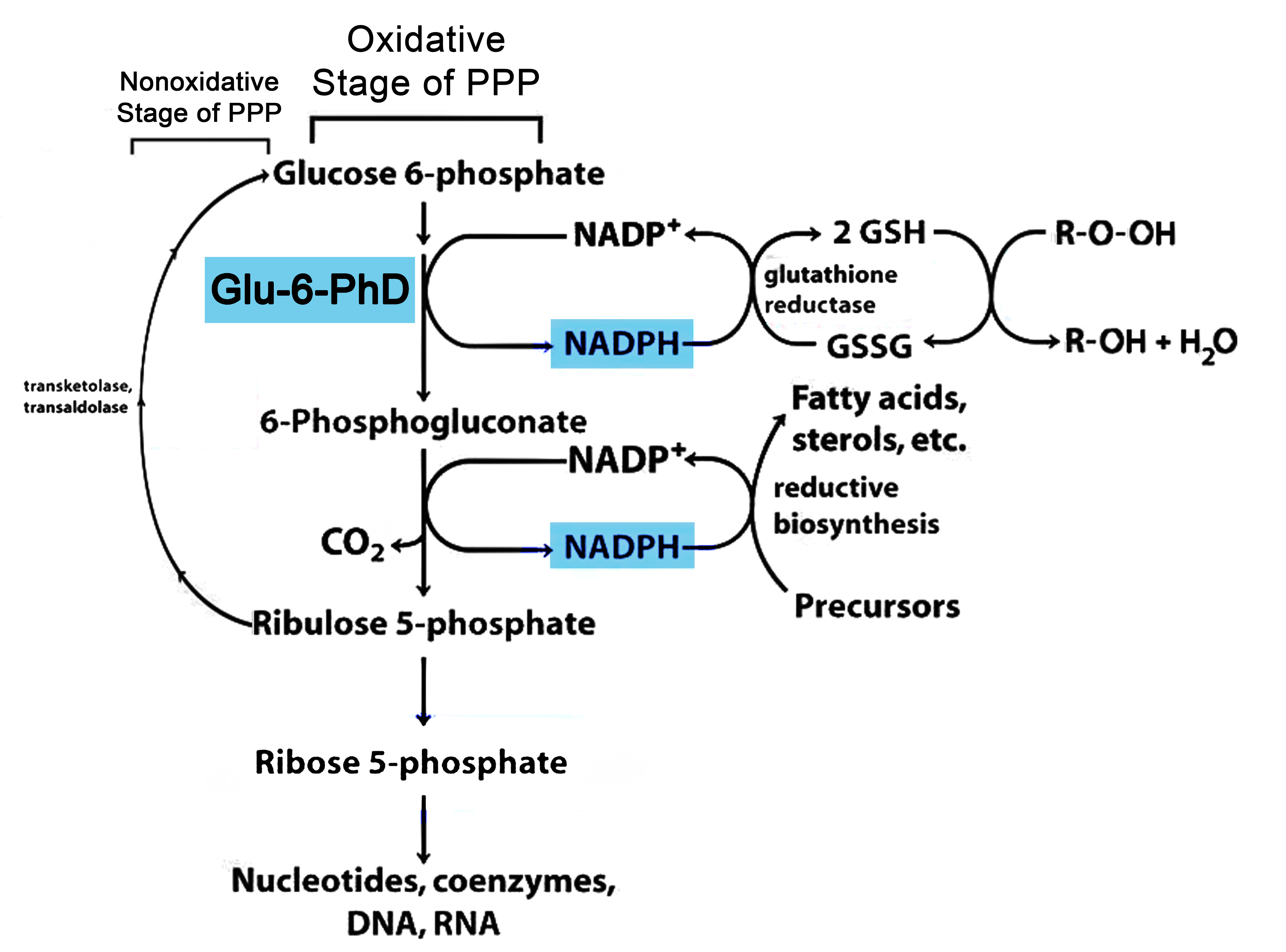
Glucose 6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the metabolism of glucose in our bodies. It is involved in the pentose phosphate pathway, which is a major pathway for the generation of NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). NADPH is essential for several important biological processes, including the reduction of oxidized glutathione and the production of fatty acids and cholesterol.
Glucose 6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Structure and Function
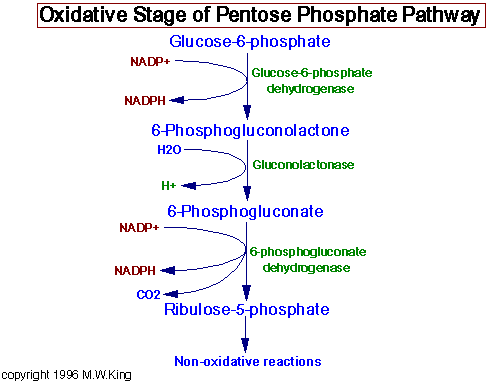 The structure of G6PD consists of a dimeric protein, where each monomer is composed of three major domains: the coenzyme-binding domain, the substrate-binding domain, and the catalytic domain. The coenzyme-binding domain binds to NADP+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) and plays a critical role in the catalytic activity of the enzyme. The substrate-binding domain binds to glucose-6-phosphate, the substrate of G6PD, and facilitates its conversion to 6-phosphoglucono-delta-lactone. Finally, the catalytic domain contains the active site of the enzyme, where the chemical reactions take place.
The structure of G6PD consists of a dimeric protein, where each monomer is composed of three major domains: the coenzyme-binding domain, the substrate-binding domain, and the catalytic domain. The coenzyme-binding domain binds to NADP+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) and plays a critical role in the catalytic activity of the enzyme. The substrate-binding domain binds to glucose-6-phosphate, the substrate of G6PD, and facilitates its conversion to 6-phosphoglucono-delta-lactone. Finally, the catalytic domain contains the active site of the enzyme, where the chemical reactions take place.
Importance of Glucose 6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase
 G6PD is a key enzyme in red blood cells and other tissues. Its role in red blood cells is particularly crucial as it provides the necessary reducing power to protect the cell from oxidative stress. Red blood cells are exposed to oxidative stress caused by reactive oxygen species, which can damage cellular structures and components. G6PD catalyzes the conversion of glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphoglucono-delta-lactone, producing NADPH in the process. NADPH, in turn, helps regenerate the reduced form of glutathione, a major intracellular antioxidant, and protects red blood cells from oxidative damage.
G6PD is a key enzyme in red blood cells and other tissues. Its role in red blood cells is particularly crucial as it provides the necessary reducing power to protect the cell from oxidative stress. Red blood cells are exposed to oxidative stress caused by reactive oxygen species, which can damage cellular structures and components. G6PD catalyzes the conversion of glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphoglucono-delta-lactone, producing NADPH in the process. NADPH, in turn, helps regenerate the reduced form of glutathione, a major intracellular antioxidant, and protects red blood cells from oxidative damage.
In addition to its antioxidant role, G6PD is also important for other physiological processes. It acts as a source of NADPH for fatty acid synthesis, a process essential for membrane and lipid production. Moreover, G6PD is involved in the production of ribose-5-phosphate, a precursor for nucleotide synthesis, which is crucial for DNA and RNA production. Thus, G6PD plays a central role in multiple biological processes, making it an essential enzyme for the proper functioning of our cells.
In conclusion, Glucose 6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase is a crucial enzyme involved in various metabolic processes in our bodies. Its role in the generation of NADPH, an important coenzyme required for antioxidant defense, fatty acid synthesis, and nucleotide production, highlights its significance. Understanding the structure and function of G6PD provides insights into the intricate mechanisms that regulate and sustain cellular homeostasis. Further research in this field can help uncover new therapeutic targets and potentially contribute to the development of treatments for diseases linked to G6PD deficiency.
If you are looking for Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) test : Results - FactDr you’ve came to the right page. We have 5 Pics about Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) test : Results - FactDr like Glucose 6 Phosphate : Central to Glucose Metabolism | Epomedicine, Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) test : Results - FactDr and also Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) test : Results - FactDr. Here it is:
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) Test : Results - FactDr
 factdr.comphosphate dehydrogenase glucose
factdr.comphosphate dehydrogenase glucose
Glucose-6- Phosphate Dehydrogenase
 sorachim.comphosphate glucose dehydrogenase
sorachim.comphosphate glucose dehydrogenase
Avens Publishing Group - Changes In Glucose-6-phosphate Dehydrogenase
 www.avensonline.orgglucose phosphate dehydrogenase role synthesis nadph 2332 jcb paroxysmal fibrillation atrial
www.avensonline.orgglucose phosphate dehydrogenase role synthesis nadph 2332 jcb paroxysmal fibrillation atrial
Glucose 6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase
 www.chem.uwec.eduGlucose 6 Phosphate : Central To Glucose Metabolism | Epomedicine
www.chem.uwec.eduGlucose 6 Phosphate : Central To Glucose Metabolism | Epomedicine
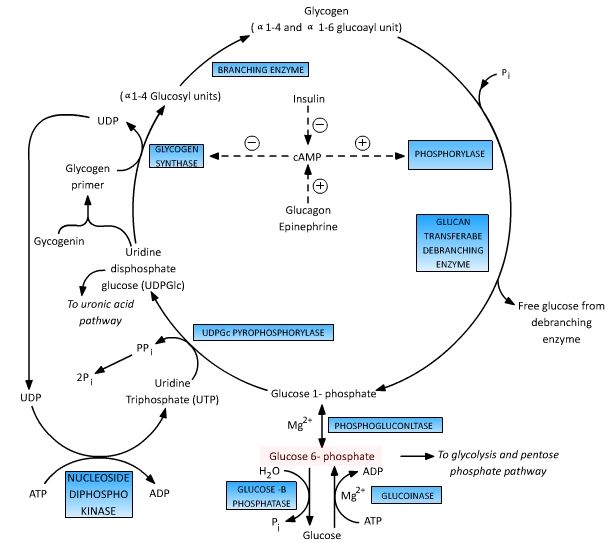 epomedicine.comglucose phosphate metabolism glycogen enzyme glycolysis fate phosphorylase central epomedicine into formation converts
epomedicine.comglucose phosphate metabolism glycogen enzyme glycolysis fate phosphorylase central epomedicine into formation converts
Glucose-6- phosphate dehydrogenase. Glucose phosphate dehydrogenase role synthesis nadph 2332 jcb paroxysmal fibrillation atrial. Glucose 6 phosphate : central to glucose metabolism